The Evolving Challenge of CAPTCHAs: Humans vs. AI
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding CAPTCHAs
CAPTCHAs, those frustrating tests that verify if you're a human, have become commonplace across various websites. They are designed to prevent malicious bots from exploiting online platforms. These bots can automate tasks, such as consuming server resources, posting spam, and even creating fake accounts. Thus, CAPTCHAs, which stand for Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart, have emerged as a necessary line of defense.
As a computer scientist, I view CAPTCHAs as a vital tool for safeguarding websites, enhancing cybersecurity, and improving user experiences—at least in the short run. For instance, during denial-of-service attacks, where servers are overwhelmed, CAPTCHAs can block automated bots from launching these attacks or engaging in other fraudulent activities, like sending spam or creating bogus accounts. Financial institutions, in particular, rely on CAPTCHAs to thwart bots attempting to compromise customer data and ensure the integrity of online voting and surveys.
Section 1.1: The Mechanism Behind CAPTCHAs
CAPTCHAs present challenges that are straightforward for humans but complicated for bots. There are various forms of CAPTCHAs, including text-based, image-based, audio-based, and behavior-based tests.
Text-based CAPTCHAs have been prevalent since the dawn of the internet. They require users to decipher distorted text and input it correctly. Some variants involve solving simple arithmetic problems, like "18+5" or "23–7." However, advancements in optical character recognition, driven by deep learning technologies, have rendered these methods less effective.
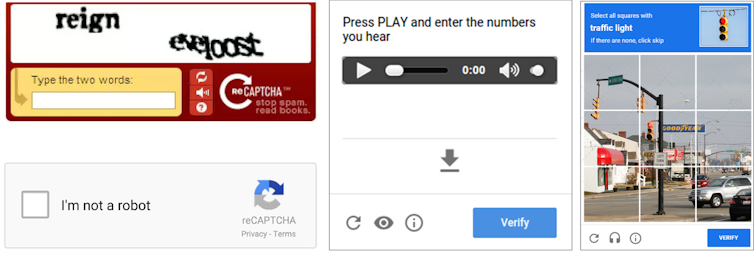
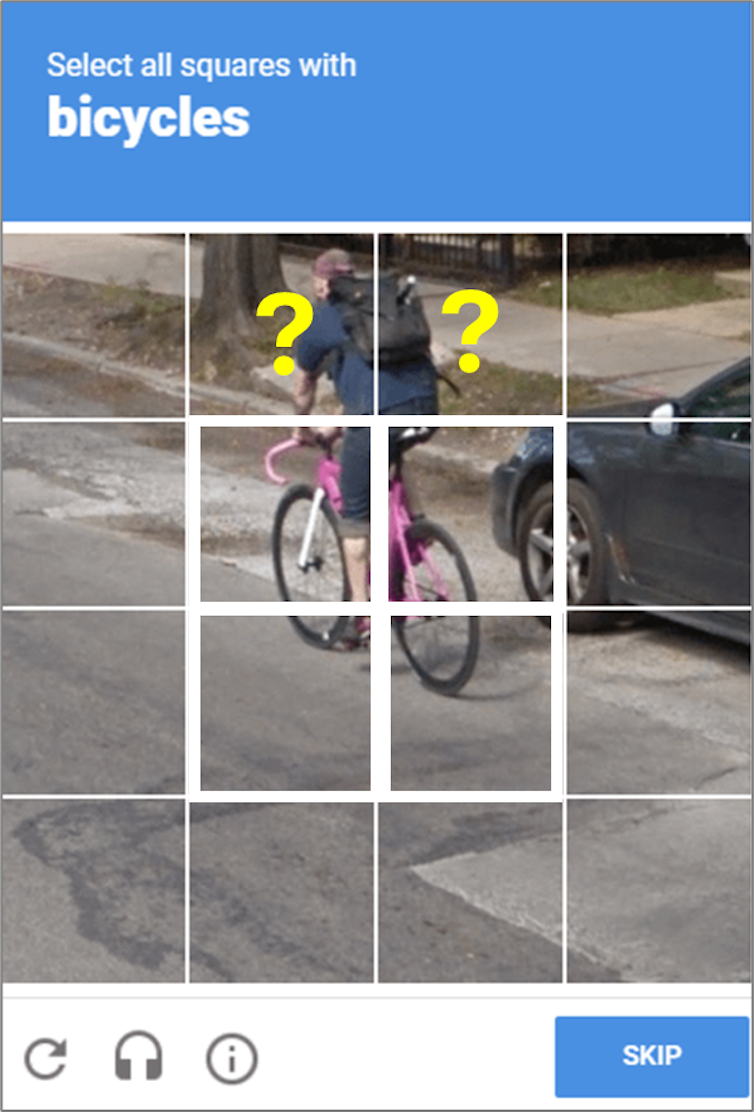
As text becomes more distorted to thwart bots, humans may ironically struggle to answer correctly. Audio CAPTCHAs, where users listen to a series of spoken numbers or letters, also present difficulties, especially when hindered by background noise or distorted audio quality. Image-based CAPTCHAs require users to identify specific items in a series of images, such as clicking on all blocks that show traffic lights. While this method plays to human visual strengths, it can still confuse users.

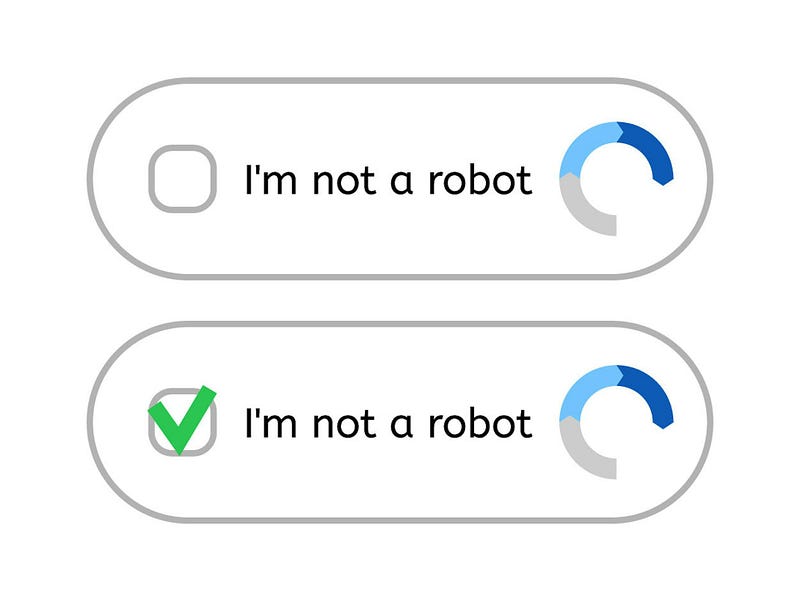
Behavior-based CAPTCHAs assess user actions, such as mouse movements and typing patterns. A widely used variant, reCAPTCHA, prompts users to check a box stating "I am not a robot" while analyzing their interactions to distinguish between human and bot behavior.
Section 1.2: The AI Challenge
The ongoing battle between AI and CAPTCHAs has intensified. Modern AI employs deep learning and computer vision techniques, making it increasingly capable of circumventing CAPTCHA tests. For example, enhanced optical character recognition can easily decode text-based CAPTCHAs, while advanced speech recognition can bypass audio tests. Similarly, AI models trained on extensive image datasets can solve image-based CAPTCHAs with remarkable accuracy.
However, CAPTCHA developers are countering this trend by creating more sophisticated CAPTCHA systems. For instance, reCAPTCHA evaluates user interactions to calculate the likelihood of their humanity.
Ironically, humans often assist AI in overcoming CAPTCHAs. Click farms employ numerous low-wage workers to click on ads, follow accounts, write fake reviews, and solve CAPTCHAs, ultimately helping AI systems mimic human behavior to outsmart these security measures.
The video "Why CAPTCHAs Are Getting Harder" delves into the challenges CAPTCHAs face in the age of advanced AI, illustrating how these tests must evolve to remain effective.
Chapter 2: The Future of CAPTCHAs
Looking ahead, the future of CAPTCHAs is likely to be shaped by the continual advancements in AI. Traditional CAPTCHA methods are becoming less effective, prompting a shift towards systems that analyze user behavior more intricately. This shift may include biometric CAPTCHAs, utilizing facial recognition or fingerprint scans, although these methods raise privacy concerns.
Moreover, blockchain technology may emerge as a substitute for CAPTCHAs, using verifiable credentials to authenticate users securely. These credentials, issued by trusted entities and stored in digital wallets, ensure that interactions are conducted by verified humans rather than bots.
The next generation of CAPTCHAs may work in real time alongside AI systems, constantly adapting to outpace automated threats.
This article is sourced from The Conversation, a nonprofit news organization dedicated to providing context and clarity on current events. Learn more about them or subscribe to their newsletter for weekly updates.
Tam Nguyen acknowledges funding from the National Science Foundation, Lam Research, and NVIDIA.
The video "Stop Junk Traffic & Spam Conversions in Google Ads" offers insights into how to improve advertising strategies and safeguard against unwanted automated interactions.