Discovering a Second White Dwarf Pulsar: A Leap in Stellar Science
Written on
Chapter 1: Stellar Evolution and New Discoveries
The recent identification of a second white dwarf pulsar is a groundbreaking development in the field of stellar evolution. This pulsar, which rotates at an astonishing rate of 300 times faster than Earth, provides deeper insights into the life cycles of stars.
White dwarfs and pulsars represent two distinct categories of stellar remnants. White dwarfs are formed from the evolution of low- to medium-mass stars and are primarily composed of electron-degenerate matter. In contrast, pulsars emerge from the explosive deaths of massive stars, consisting of tightly packed neutrons.
Section 1.1: Characteristics of White Dwarfs and Pulsars
White dwarfs typically exhibit slow rotation rates, generate minimal electromagnetic radiation, and do not possess strong magnetic fields. Conversely, pulsars are characterized by rapid rotation, emit beams of radiation across various wavelengths, and have intense magnetic fields.
Subsection 1.1.1: Observational Differences
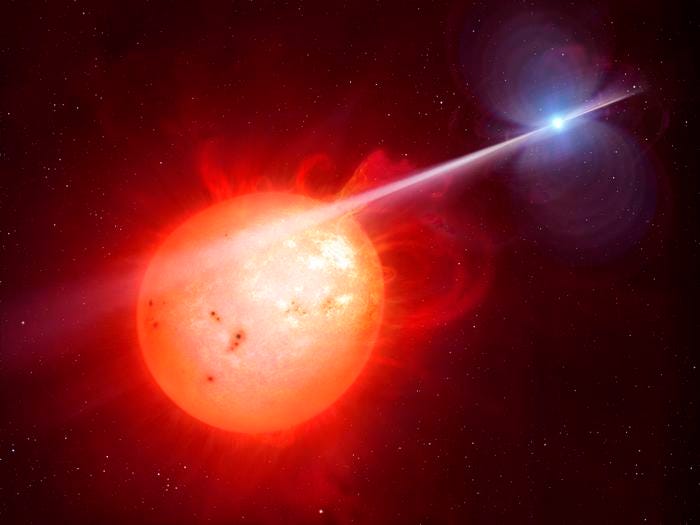
While white dwarfs appear as faint and hot celestial objects, often found in binary systems, pulsars are energetic sources detected through their periodic signals, which allow for accurate measurements of their rotational characteristics.
The University of Warwick has spearheaded pioneering research that led to the identification of this second rare type of white dwarf pulsar. This remarkable discovery enhances our comprehension of stellar evolution and provides new perspectives on white dwarf star systems.
A gas giant orbiting a tiny white dwarf is the first of its kind
This peculiar star system presents us with another cosmic riddle — the size of the exoplanet and its survival around the...
In an innovative study supported by the UK Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC), researchers have unveiled findings on a newly identified white dwarf pulsar designated as J191213.72–441045.1. This discovery is significant as it represents only the second case of such a star system ever recorded, following the first instance of AR Scorpii (AR Sco) in 2016.

“This confirms the existence of more white dwarf pulsars, as previously predicted by theoretical models. The dynamo model's predictions were substantiated by the discovery of J1912–4410.”
~ Dr. Ingrid Pelisoli, Lead Researcher

The research delves into the “dynamo model,” a prominent theory positing that white dwarfs possess exceptionally powerful electrical generators akin to Earth's core, which explain their strong magnetic fields. This new discovery provides an opportunity to validate the predictions associated with this theory.
Having originated from extreme temperatures, white dwarfs gradually cool over billions of years. The relatively low temperature of J1912–4410 suggests an advanced age. Located 773 light years from Earth, this white dwarf pulsar rotates at an impressive rate 300 times faster than our planet, while its size is comparable to that of Earth, with a mass at least equal to that of the Sun.
A white dwarf star & a pulsar is dragging the space-time continuum
The two dense stars are validating the phenomenon predicted in Einstein’s general theory of relativity.
A mere teaspoon of material from a white dwarf would weigh around 15 tons. Moreover, the research team made an intriguing observation about J1912–4410 — it completes a full rotation every five minutes. As anticipated by the scientists, the gravitational force of the white dwarf significantly influences its companion star, aligning with their predictions.
By analyzing data from various astronomical surveys, the team successfully identified J1912–4410, utilizing a search strategy focused on systems exhibiting similarities to AR Sco. Promising candidates were further examined using ULTRACAM, an ultra-fast camera capable of capturing 500 images per second.
This advanced imaging technology plays a crucial role in capturing the rapid luminosity fluctuations characteristic of white dwarf pulsars, making it a vital tool for detecting such high-speed astronomical phenomena. The complete findings of this research were published in the Journal of Nature Astronomy.
The first video titled "Stellar Corpses: White Dwarfs, Novae, Neutron Stars, and Pulsars" explores the various types of stellar remnants, including white dwarfs and pulsars, and discusses their significance in the cosmos.
The second video, "14: Mysterious white dwarf pulsar discovered," delves into the implications of the recent discoveries in white dwarf pulsar research and their impact on our understanding of stellar evolution.
Read more stories like this and others by Faisal Khan on Medium.
Stay informed with the content that matters — Join my Mailing List.