Amtrak's Journey: Challenges and Triumphs in Passenger Rail
Written on
Introduction to Amtrak
Dear Reader,
I'm thrilled to share a narrative about a national railroad company that plays a vital role in providing both passenger and freight services across the United States—Amtrak. Established in 1971, Amtrak operates inter-city rail services, connecting numerous cities in the U.S. and extending into three Canadian provinces.
Inter-city rail services are designed for express passenger travel, linking cities over greater distances than typical commuter or regional trains.
As a quasi-public entity, Amtrak was created to manage many of the U.S. passenger rail routes. While it receives a mix of state and federal funding, it operates with the aim of profitability, situated just one block west of Union Station in Washington, D.C.
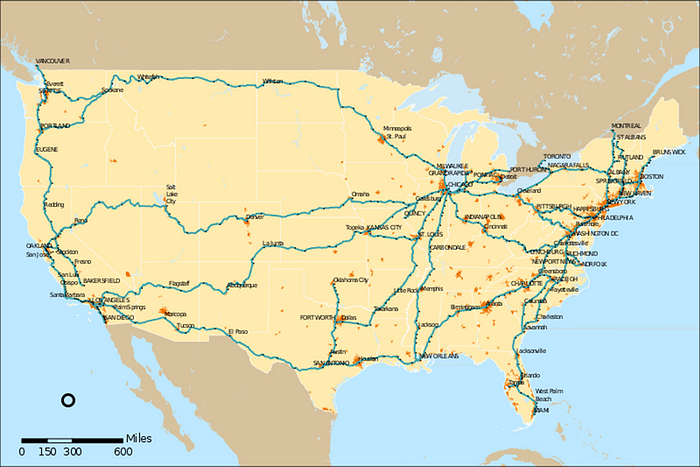
Amtrak's Operational Landscape
Amtrak boasts a network that encompasses 500 stations and spans 21,400 miles of track, of which it owns 623 miles outright and operates an additional 132 miles. Certain stretches of track allow trains to reach speeds of up to 150 mph.
In 2022, Amtrak recorded 22.9 million passengers and generated $2.1 billion in revenue, employing around 17,100 individuals. Daily commuters account for nearly 87,000 of the passengers utilizing over 300 Amtrak trains. A significant portion of riders—approximately two-thirds—originates from the nation's ten largest metropolitan areas, with 83% traveling routes shorter than 400 miles.
The Decline of Private Passenger Services
In 1916, commercial intercity rail travel in the U.S. saw 42 million passengers, representing around 98% of rail users. However, the advent of commercial buses, air travel, and personal vehicles in the 20th century caused a downturn in train travel. Though streamlined diesel trains like the Pioneer Zephyr gained popularity, they could not reverse the trend.
By 1940, railroads accounted for 67% of commercial passenger miles, a stark drop from 98% in 1916.
During World War II, troop movements and gas rationing led to a temporary increase in rail traffic, with railroads achieving a 74% market share in 1945. However, post-war revitalization efforts fell short, and by 1957, the rail market share had plummeted to 32%. The Great Depression had already set the stage for financial struggles, with railroads losing $723 million by 1957.
Debates surrounding the causes of this decline were widespread. The establishment of the National Highway System and government-funded airports directly competed with railroads, which were responsible for maintaining their infrastructure. Moreover, a growing American affinity for automobiles and restrictive Progressive Era regulations further exacerbated the situation.
Passenger service route miles dwindled from 107,000 in 1958 to just 49,000 by 1970, culminating in significant losses when the U.S. Post Office shifted mail transport from rail to other modes.
The Birth of Amtrak
Proposals to rescue passenger rail services proliferated, with the 1961 Doyle Report advocating for a unified rail service. However, earlier initiatives did not gain traction until the Rail Passenger Service Act was enacted in October 1970, which established the National Railroad Passenger Corporation (NRPC).
This act aimed to relieve railroads from the obligation to provide passenger service, allowing the NRPC to step in and manage intercity train operations starting May 1, 1971. Though the NRPC was initially met with skepticism, it was created to ensure the sustainability of passenger rail.
Despite early challenges, including financial mismanagement, Amtrak has become a critical component of U.S. transportation.
Conclusion
This article is just the first of a six-part series exploring Amtrak's history, its accomplishments, leadership figures, and the future of passenger rail. If you found this piece insightful, please consider showing your support by following my writing journey on Medium. Your engagement encourages me to continue sharing these stories.
Thank you for taking the time to read, and I hope to see you in the next installment!